- 7 min
Ever wondered how big industries like power plants, water treatment facilities, and manufacturing plants keep everything running so smoothly? It’s not magic – it’s SCADA or, Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition, and it’s a complex yet fascinating system that plays a massive role in our daily lives.
The Basics of SCADA
In a nutshell, SCADA systems are used to monitor and control industrial processes. They collect data from various sensors and machines, send that data to a central computer, and then use the information to make real-time, automated decisions. You can think of SCADA as the ultimate multitasker – overseeing operations, optimising performance, and ensuring everything stays on track.
Breaking Down the Components
SCADA might sound like a single entity, but it’s actually composed of several key components:
1. Sensors: These little gadgets measure different parameters like temperature, pressure, or flow rates, and can be thought of as the eyes and ears of the SCADA system. They are strategically placed at various points within a process to capture critical data points.
2. RTUs (Remote Terminal Units): RTUs serve as intermediaries between the sensors and the central system. They collect data from sensors and can even execute simple commands based on predefined criteria. Think of RTUs as data collectors and messengers.
3. PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers): Similar to RTUs but more powerful, PLCs execute control programs to automate processes. These are highly flexible and can be programmed to perform complex operations, making them indispensable in modern industrial settings.
4. Communication Network: This is the bridge that allows data to travel from the sensors to the central computer. It can involve various communication protocols and mediums, including wired and wireless networks, ensuring that data flows seamlessly and reliably.
5. HMI (Human-Machine Interface): Think of this as the control dashboard where operators can monitor and interact with the system. The HMI provides a graphical representation of the processes, allowing operators to make informed decisions and interventions.
Now that we’ve unpacked its components, let’s explore how SCADA works in action.
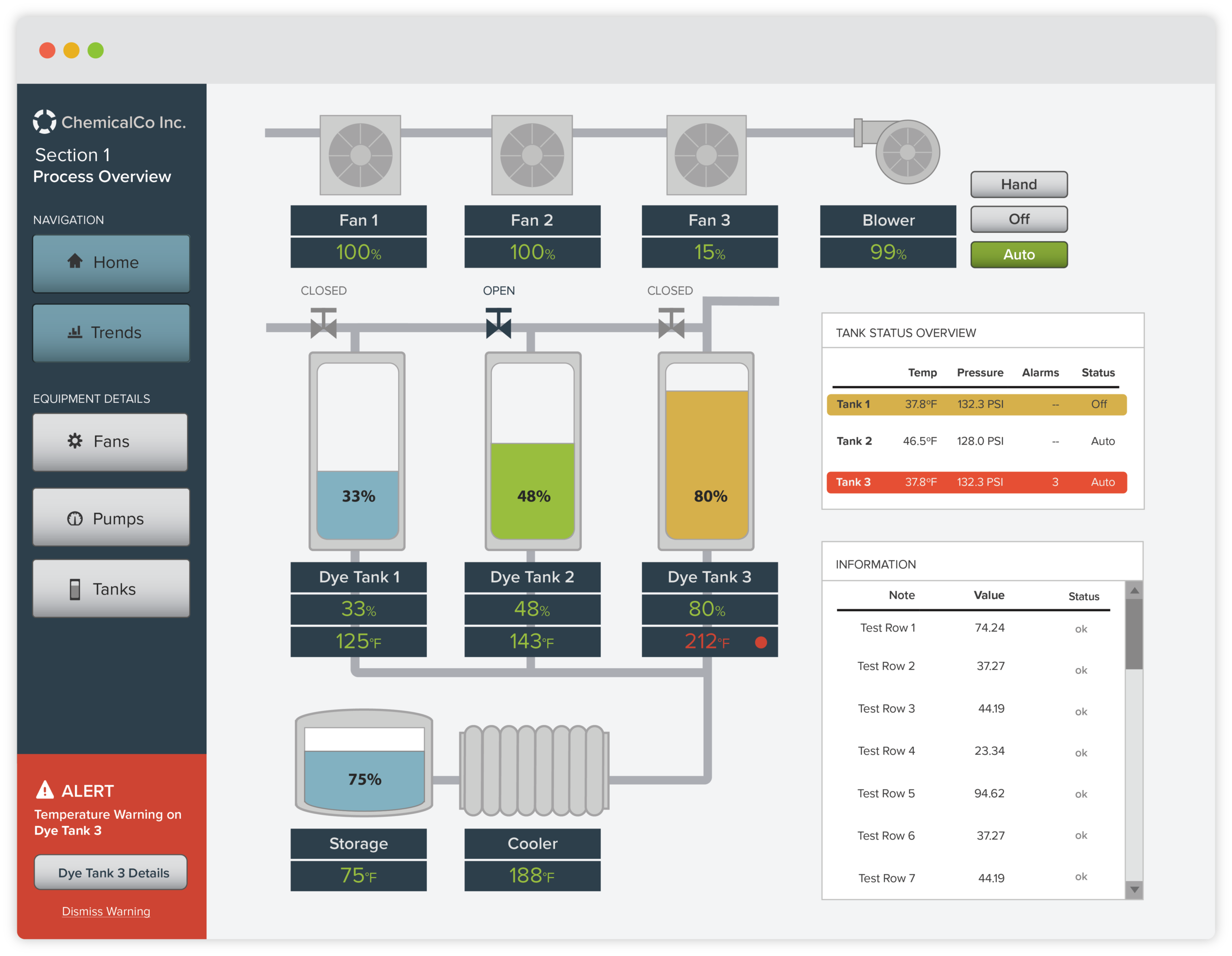
How SCADA Systems Operate
Imagine you’re managing a water treatment plant. Your SCADA system constantly collects data on water levels, pressure, and chemical composition. If any value strays from the optimal range, SCADA sends out alerts and can even make immediate adjustments like opening valves or adjusting pump speeds to keep everything balanced.
This real-time monitoring and control prevent issues before they become full-blown problems, saving time, money, and resources. Essentially, SCADA systems act as the nerve centre of any large-scale operation, ensuring efficiency and safety. The automatic nature of SCADA is particularly beneficial in environments where quick responses are crucial, such as in emergencies or during peak operational periods.
Real-Life Applications of SCADA
SCADA systems are used across various industries to enhance productivity and safety. Here are a few examples:
Energy Management
In power grids, SCADA systems monitor electrical currents, manage load distribution, and detect faults in the network. This ensures a stable and continuous supply of electricity. For instance, SCADA can balance the load across multiple power plants, ensuring that every plant is adequately funded while others remain underutilised. It also helps in integrating renewable energy sources, balancing them against the inconsistencies they might introduce to the grid.
Manufacturing
In manufacturing, SCADA oversees production lines, manages machinery, and ensures that products are made to specifications. This maximises efficiency and reduces waste. By tracking every step of the production process, SCADA systems can identify bottlenecks, streamline workflows, and ensure that machinery is operating within optimal parameters.
Water and Wastewater Management
Water treatment plants use SCADA to monitor water quality, manage the filtration process, and control pumps and valves. This keeps our water clean and safe to drink. SCADA systems can also help in leak detection and energy management within the plants, ensuring that resources are used efficiently and costs are minimised.
Ignition by Inductive Automation: A SCADA System Worth Knowing
With its innovative features and intuitive interface, Ignition is a standout SCADA platform that sets itself apart from the rest. What makes it truly unique is the balance it strikes between user-friendliness and powerful capabilities. It’s rare to find a platform that can seamlessly connect to any system or device, but Ignition does just that. This all-in-one solution offers unparalleled versatility, making it the perfect fit for businesses of any size, from small startups to large enterprises. And with its scalable options, Ignition can adapt to your changing needs as your business grows.
Key Features
1. Unlimited Licensing: One of Ignition’s standout features is its unlimited licensing model. This means you’re not restricted by tag limits or client counts, allowing for unlimited scalability and growth.
2. Web-Based Deployment: Ignition is entirely web-based, which means you can access your SCADA system from any device with an internet connection. This offers unprecedented flexibility and mobility, especially useful in today’s increasingly remote and interconnected work environments.
3. Real-Time Data: With Ignition, you can visualise and analyse real-time data, ensuring you have the most up-to-date information at your fingertips. This real-time access to data allows for quicker decision-making and improves overall operational responsiveness.
4. Security: Security is paramount in SCADA systems, and Ignition takes this seriously with robust security protocols to protect your data and operations. These include user authentication, data encryption, and compliance with industry standards.
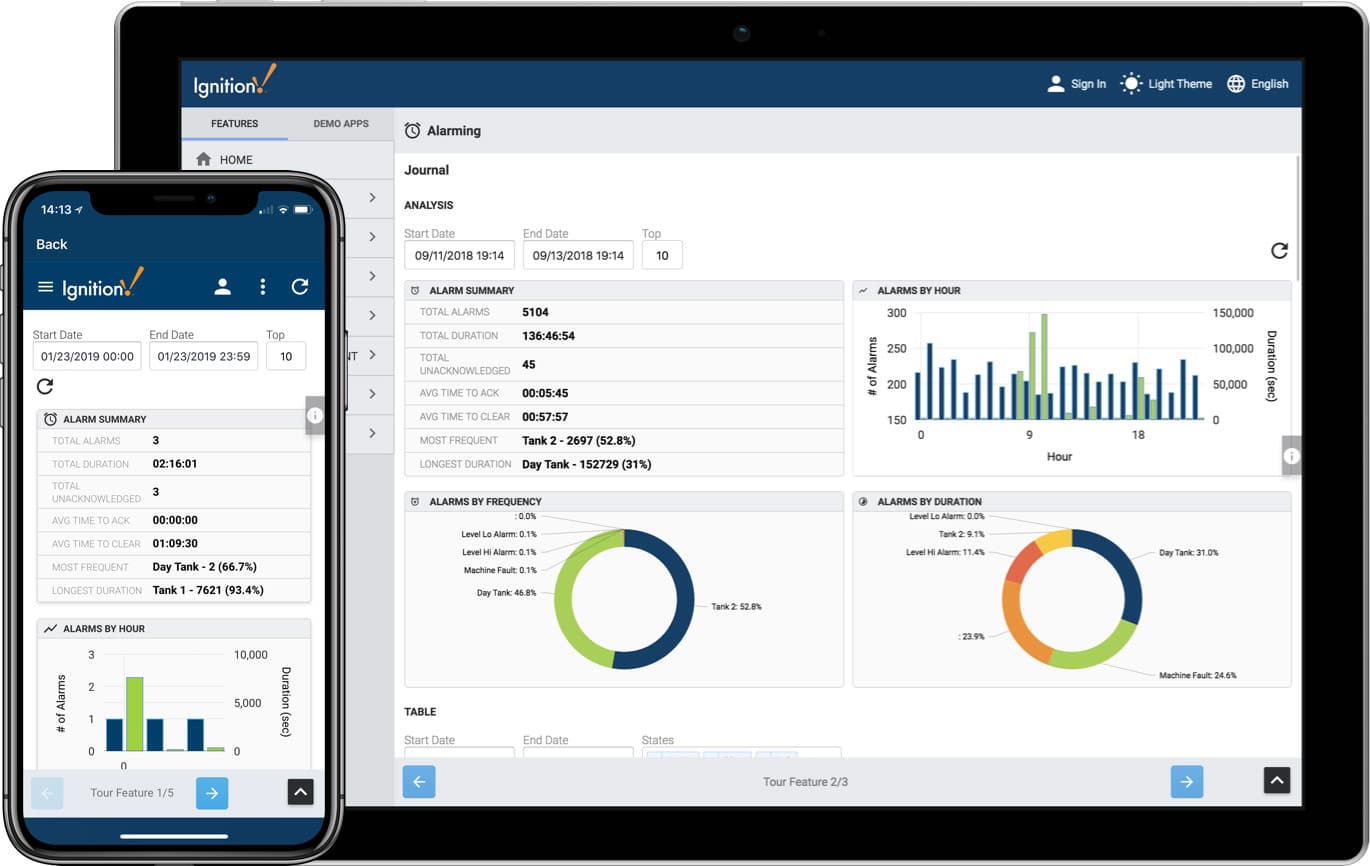
Use Cases
Many industries have leveraged Ignition for their SCADA needs. For instance, water treatment facilities have used Ignition to streamline their monitoring systems, improving water quality and ensuring efficient resource management. Manufacturing plants have implemented Ignition to optimise production lines, boost productivity, and reduce downtime. The flexibility of Ignition means it can be tailored to meet the specific needs of different industries, providing a customised approach to automation and data management.
The Future of SCADA
SCADA technology is continually evolving, with advancements in automation, IIoT, and AI shaping its future. Modern SCADA systems are becoming smarter, more efficient, and more integrated with other technologies. As more industries embrace digital transformation, SCADA will undoubtedly play an even more critical role in our industrial landscape.
The introduction of IoT devices has allowed for more granular data collection, providing SCADA systems with a more comprehensive view of operations. This integration facilitates predictive maintenance, where potential issues are identified and addressed before they can escalate into major problems. Moreover, advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning are enabling SCADA systems to make more informed and autonomous decisions, further reducing the need for human intervention.
SCADA systems might work silently behind the scenes, but their impact is profound, ensuring that our daily lives run smoothly and safely. Whether you’re a tech enthusiast, an industry professional, or just someone with a curious mind, understanding SCADA gives you insight into the backbone of industrial automation.
If you think your company could benefit from a SCADA like Ignition, or you just want to know more about Ignition, click here.






